Median income
Median income is the amount that divides the income distribution into two equal groups, half having income above that amount, and half having income below that amount. Mean income (average) is the amount obtained by dividing the total aggregate income of a group by the number of units in that group. Mode income is the most frequently occurring income in a given income distribution.
Median income can be calculated by household income, by personal income, or for specific demographic groups.
Contents
1 Gross median household income by country
2 Median equivalent adult income
3 Median household income and the US economy
4 Per capita income
4.1 As a measure of prosperity
4.2 Critics
5 See also
6 References
Gross median household income by country
@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;max-width:none!important.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center
In 2013, Gallup published a list of countries with median annual household income, based on a self-reported survey of approximately 2000 adults from each country.[1] Using median, rather than mean income, results in a much more accurate picture of the typical income of the middle class since the data will not be skewed by gains and abnormalities in the extreme ends. The figures are in international dollars using purchasing power parity and are based on responses from 2006 to 2012 inflation adjusted to 2010 levels. Below is a list of the top 30 countries. The figures do not take taxes and social contributions into account.[1][2]
Please note that the list below does not correspond to citizens of each country, but to all its residents. States rich in fossil fuels such as Qatar and Kuwait have a very large gap in terms of median annual earnings of citizens and non-citizens (reaching more than tenfold).
|
Median equivalent adult income
The annual median equivalence disposable household income for selected OECD countries is shown in the table below. This is the disposable income of an equivalent adult in a household in the middle of the income distribution in a year.
Data are in United States dollars at current prices and current purchasing power parity for private consumption for the reference year.
|
- An academic study on the Census income data claims that when correcting for underreporting, U.S. gross median household income was 15% higher in 2010 (table 3).[4]
Median household income and the US economy
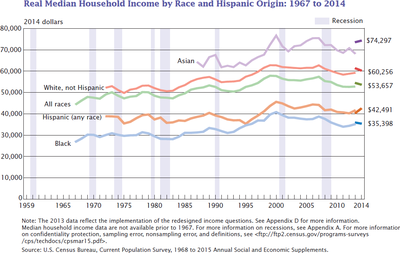
This graph shows the income since 1970 of different racial and ethnic groups in the United States (in 2014 dollars).[5]
Since 1980, U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) per capita has increased 67%,[6] while median household income has only increased by 15%. Median household income is a politically sensitive indicator. Voters can be critical of their government if they perceive that their cost of living is rising faster than their income.
The early-2000s recession began with the bursting of the dot-com bubble and affected most advanced economies including the European Union, Japan and the United States. An economic recession will normally cause household incomes to decrease, often by as much as 10%.
The late-2000s recession began with the bursting of the U.S. housing bubble, which caused a problem in the dangerously exposed sub prime-mortgage market. This in turn triggered a global financial crisis. In constant price, 2011 American median household income was 1.13% lower than what it was in 1989. This corresponds to a 0.05% annual decrease over a 22-year period.[7] In the mean time, GDP per capita has increased by 33.8% or 1.33% annually.[8]
A study on US Census income data claims that when using the national accounting methodology, U.S. gross median household income was $57,739 in 2010 (table 3).[9]
In 2015, the US median household income spiked 5.2 per cent, reaching $56,000, making it the first annual hike in median household income since the start of the Great Recession.[10]
Per capita income

Countries by GNI (PPP) per capita in 2016
Per capita income (PCI) or average income measures the average income earned
per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.[11][12]
As a measure of prosperity
Per capita income is national income/total population.
Per capita income is often used to measure an area's average income. This is used to see the wealth of the population with those of others. Per capita income is often used to measure a country's standard of living. It is usually expressed in terms of a commonly used international currency such as the euro or United States dollar, and is useful because it is widely known, is easily calculable from readily available gross domestic product (GDP) and population estimates, and produces a useful statistic for comparison of wealth between sovereign territories. This helps to ascertain a country's development status. It is one of the three measures for calculating the Human Development Index of a country.
- United States
In the United States, it is defined by the U.S. Census Bureau as the following: "Per capita income is the mean money income received in the past 12 months computed for every man, woman, and child in a geographic area."[13] (Children are counted if they are at least 15 years old.)
Critics
Critics claim that per capita income has several weaknesses in measuring prosperity:[14]
- Comparisons of per capita income over time need to consider inflation. Without adjusting for inflation, figures tend to overstate the effects of economic growth.
- International comparisons can be distorted by cost of living differences not reflected in exchange rates. Where the objective is to compare living standards between countries, adjusting for differences in purchasing power parity will more accurately reflect what people are actually able to buy with their money.
- It is a mean value and does not reflect income distribution. If a country's income distribution is skewed, a small wealthy class can increase per capita income substantially while the majority of the population has no change in income. In this respect, median income is more useful when measuring of prosperity than per capita income, as it is less influenced by outliers.
- Non-monetary activity, such as barter or services provided within the family, is usually not counted. The importance of these services varies widely among economies.
- Per capita income does not consider whether income is invested in factors likely[according to whom?] to improve the area's development, such as health, education, or infrastructure.
See also
- List of countries by average wage
- List of U.S. states by income
- Mean household income
- Income distribution
- Income quintiles
- Household income in the United States
- International Ranking of Household Income
- List of countries by GNI (nominal, Atlas method) per capita
- List of countries by GNI (PPP) per capita
- Median
- Median household income in Australia and New Zealand
- Median income per household member
- Places in the United States with notable demographic characteristics
- Poverty in the United States
References
^ abcd "Worldwide, Median Household Income About $10,000". Gallup.
^ "New Measures of Global Income From the Gallup World Poll". Gallup. Gallup. December 13, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2017.
^ http://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=IDD
^ https://bea.gov/about/pdf/Fixler_Johnson.pdf
^ DeNavas-Walt, Carmen; Proctor, Bernadette D.; Smith, Jessica C. (September 2012). "Real Median Household Income by Race and Hispanic Origin: 1967 to 2010". Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2014 (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. p. 8.
^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org.
^ "Income Data".
^ "Bureau of Economic Analysis". www.bea.gov.
^ http://bea.gov/about/pdf/Fixler_Johnson.pdf
^ Picchi, Aimee (September 13, 2016). "Median Household income increases". CBS News. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
^ Per capita income The Free Dictionary
^ Income Per Capita Definition, Investopedia
^ U. S. Census Bureau – Per Capita Income, American Community Survey Archived 2015-10-04 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "The Economics of Well-Being" Harvard Business Review 2011
 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP

