Google Chrome
 Google Chrome on Windows 10 | |||||||||||||||||
| Developer(s) | Google LLC | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial release | September 2, 2008 (2008-09-02) | ||||||||||||||||
Stable release(s) [±] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Preview release(s) [±] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Development status | Active | ||||||||||||||||
| Written in | C, C++, Java, JavaScript, Python[8][9][10] | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating system |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Engines | Blink (WebKit on iOS), V8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Platform | IA-32, x64, ARMv7, ARMv8-A | ||||||||||||||||
| Available in | 47 languages[12] | ||||||||||||||||
List of languages Afrikaans, Amharic, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (Hong Kong), Chinese (PRC), Chinese (Taiwan), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English (AU), English (UK), English (US), Estonian, Filipino, Finnish, French (Canada), French (France), German, Greek, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Latvian, Lithuanian, Malay, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil), Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish (Latin America), Spanish (Spain), Swahili, Swedish, Thai, Turkish, Ukrainian, Zulu | |||||||||||||||||
| Type | Web browser, mobile browser | ||||||||||||||||
| License | Proprietary freeware, based on open source components.[13][note 1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.google.com/chrome/ | ||||||||||||||||
Google Chrome (commonly known simply as Chrome) is a freeware web browser developed by Google LLC.[13] It was first released on September 2, 2008, for Microsoft Windows, and was later ported to Linux, macOS, iOS and Android. Google Chrome is also the main component of Chrome OS, where it serves as a platform for running web apps.
Google releases the majority of Chrome's source code as the Chromium open-source project;[14][15] however, Chrome itself is proprietary software.[16][13] One component that is not open-source is the built-in Adobe Flash Player (that Chrome has disabled by default since September 2016[17]). Chrome used the WebKit layout engine until version 27. As of version 28, all Chrome ports except the iOS port use Blink, a fork of the WebKit engine.[18][19][20]
As of 2018[update], StatCounter estimates that Google Chrome has a 66% worldwide usage share of web browsers as a desktop browser.[21] It also has 56% market share across all platforms combined,[22] because it has over 50% share on smartphones; and thus Chrome is the most used browser in virtually all countries (most exceptions in Africa).[23] Its success has led to Google expanding the "Chrome" brand name on various other products such as Chrome OS, Chromecast, Chromebook, Chromebit, Chromebox and Chromebase.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Announcement
1.2 Public release
1.3 Development
1.4 Version history
2 Features
2.1 Bookmarks and settings synchronization
2.2 Web standards support
2.3 Security
2.3.1 Security vulnerabilities
2.3.2 Malware blocking and ad blocking
2.3.3 Plugins
2.4 Privacy
2.4.1 Incognito mode
2.4.2 Listening capabilities
2.4.3 User tracking concerns
2.4.4 Do Not Track
2.5 Speed
2.6 Stability
2.7 User interface
2.8 Desktop shortcuts and apps
2.8.1 Chrome Web Store
2.9 Extensions
2.9.1 Notable examples
2.10 Themes
2.11 Automatic web page translation
2.12 Release channels, cycles and updates
2.12.1 Release version numbers
2.13 Color management
2.14 T-Rex
3 Platforms
3.1 Compatibility
3.2 Android
3.3 Chrome OS
3.4 iOS
3.5 Linux
3.6 Windows
3.7 macOS
4 Reception
5 Usage
5.1 Market share
5.2 Enterprise deployment
5.3 Chromium
6 Developing for Chrome
7 See also
8 Notes
9 References
10 External links
History
Google CEO Eric Schmidt opposed the development of an independent web browser for six years. He stated that "at the time, Google was a small company," and he did not want to go through "bruising browser wars." After co-founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page hired several Mozilla Firefox developers and built a demonstration of Chrome, Schmidt admitted that "It was so good that it essentially forced me to change my mind."[24]
Rumors of Google building a web browser first appeared in September 2004. Online journals and U.S. newspapers stated at the time that Google was hiring former Microsoft web developers among others. It also came shortly after the final 1.0 release of Mozilla Firefox, which was surging in popularity and taking market share from Internet Explorer, which was suffering from major security problems.[25]
Announcement
The release announcement was originally scheduled for September 3, 2008, and a comic by Scott McCloud was to be sent to journalists and bloggers explaining the features within the new browser.[26] Copies intended for Europe were shipped early and German blogger Philipp Lenssen of Google Blogoscoped[27] made a scanned copy of the 38-page comic available on his website after receiving it on September 1, 2008.[28] Google subsequently made the comic available on Google Books[29] and mentioned it on their official blog along with an explanation for the early release.[30] The product was allegedly named "Chrome" because Google wanted to minimize the chrome of the browser,[31] though this meaning was added somewhat post-hoc, the 'codename' before release apparently chosen from a connotation of speed.[32]
Public release
An early version of Chromium for Linux, explaining the difference between Chrome and Chromium
The browser was first publicly released on September 2, 2008 for Windows XP and later, with 43 supported languages, officially a beta version,[33] and as a stable public release on December 11, 2008.
On the same day, a CNET news item[34] drew attention to a passage in the Terms of Service statement for the initial beta release, which seemed to grant to Google a license to all content transferred via the Chrome browser. This passage was inherited from the general Google terms of service.[35] Google responded to this criticism immediately by stating that the language used was borrowed from other products, and removed this passage from the Terms of Service.[13]
Chrome quickly gained about 1% usage share.[30][36][37][38] After the initial surge, usage share dropped until it hit a low of 0.69% in October 2008. It then started rising again and by December 2008, Chrome again passed the 1% threshold.[39]
In early January 2009, CNET reported that Google planned to release versions of Chrome for OS X and Linux in the first half of the year.[40] The first official Chrome OS X and Linux developer previews[41] were announced on June 4, 2009, with a blog post[42] saying they were missing many features and were intended for early feedback rather than general use.
In December 2009, Google released beta versions of Chrome for OS X and Linux.[43][44] Google Chrome 5.0, announced on May 25, 2010, was the first stable release to support all three platforms.[45]
Chrome was one of the twelve browsers offered to European Economic Area users of Microsoft Windows in 2010.[46]
Development
Chrome was assembled from 25 different code libraries from Google and third parties such as Mozilla's Netscape Portable Runtime, Network Security Services, NPAPI (dropped as of version 45),[47]Skia Graphics Engine, SQLite, and a number of other open-source projects.[48] The V8 JavaScript virtual machine was considered a sufficiently important project to be split off (as was Adobe/Mozilla's Tamarin) and handled by a separate team in Denmark coordinated by Lars Bak at Aarhus. According to Google, existing implementations were designed "for small programs, where the performance and interactivity of the system weren't that important", but web applications such as Gmail "are using the web browser to the fullest when it comes to DOM manipulations and JavaScript", and therefore would significantly benefit from a JavaScript engine that could work faster.
Chrome initially used the WebKit rendering engine to display web pages. In 2013, they forked the WebCore component to create their own layout engine Blink. Based on WebKit, Blink only uses WebKit's "WebCore" components, while substituting other components, such as its own multi-process architecture, in place of WebKit's native implementation.[18]
Chrome is internally tested with unit testing, "automated user interface testing of scripted user actions", fuzz testing, as well as WebKit's layout tests (99% of which Chrome is claimed to have passed), and against commonly accessed websites inside the Google index within 20–30 minutes.[29]
Google created Gears for Chrome, which added features for web developers typically relating to the building of web applications, including offline support.[29] Google phased out Gears as the same functionality became available in the HTML5 standards.[49]
On January 11, 2011, the Chrome product manager, Mike Jazayeri, announced that Chrome would remove H.264 video codec support for its HTML5 player, citing the desire to bring Google Chrome more in line with the currently available open codecs available in the Chromium project, which Chrome is based on.[50] Despite this, on November 6, 2012, Google released a version of Chrome on Windows which added hardware-accelerated H.264 video decoding.[51] In October 2013, Cisco announced that it was open-sourcing its H.264 codecs and will cover all fees required.[52]
On February 7, 2012, Google launched Google Chrome Beta for Android 4.0 devices.[53] On many new devices with Android 4.1 and later preinstalled, Chrome is the default browser.[54]
In May 2017, Google announced a version of Chrome for augmented reality and virtual reality devices.[55]
Version history
Features
Google Chrome features a minimalistic user interface, with its user-interface principles later being implemented into other browsers. For example, the merging of the address bar and search bar into the omnibox.[56] Chrome also has a reputation for strong browser performance.[57][58]
Bookmarks and settings synchronization
Chrome allows users to synchronize their bookmarks, history, and settings across all devices with the browser installed by sending and receiving data through a chosen Google Account, which in turn updates all signed-in instances of Chrome. This can be authenticated either through Google credentials, or a sync passphrase.
Web standards support

The results of the Acid3 test on Google Chrome 4.0
The first release of Google Chrome passed both the Acid1 and Acid2 tests. Beginning with version 4.0, Chrome has passed all aspects of the Acid3 test.[59]
As of May 2011, Chrome has very good support for JavaScript/ECMAScript according to Ecma International's ECMAScript standards conformance Test 262[60] (version ES5.1 May 18, 2012). This test reports as the final score the number of tests a browser failed; hence lower scores are better. In this test, Chrome version 37 scored 10 failed/11578 passed. For comparison, Firefox 19 scored 193 failed/11752 passed and Internet Explorer 9 has a score of 600+ failed, while Internet Explorer 10 has a score of 7 failed.
In 2011, on the official CSS 2.1 test suite by standardization organization W3C, WebKit, the Chrome rendering engine, passes 89.75% (89.38% out of 99.59% covered) CSS 2.1 tests.[61]
On the HTML5 web standards test, Chrome 41 scores 518 out of 555 points, placing it ahead of the five most popular desktop browsers.[62][63] Chrome 41 on Android scores 510 out of 555 points.[64][65][66] Chrome 44 scores 526, only 29 points less than the maximum score.[67]
Security
Chrome periodically retrieves updates of two blacklists (one for phishing and one for malware), and warns users when they attempt to visit a site flagged as potentially harmful. This service is also made available for use by others via a free public API called "Google Safe Browsing API".[29]
Chrome uses a process-allocation model to sandbox tabs.[68] Using the principle of least privilege, each tab process cannot interact with critical memory functions (e.g. OS memory, user files) or other tab processes – similar to Microsoft's "Protected Mode" used by Internet Explorer 9 or greater. The Sandbox Team is said to have "taken this existing process boundary and made it into a jail." This enforces a computer security model whereby there are two levels of multilevel security (user and sandbox) and the sandbox can only respond to communication requests initiated by the user.[69] On Linux sandboxing uses the seccomp mode.[70][71]
Since 2008, Chrome has been faulted for not including a master password to prevent casual access to a user's passwords. Chrome developers have indicated that a master password does not provide real security against determined hackers and have refused to implement one. Bugs filed on this issue have been marked "WontFix".[72][73] As of February 2014[update], the Windows version asks the user to enter the Windows account password before showing saved passwords.[74]
In January 2015, TorrentFreak reported that using Chrome when connected to the internet using a VPN can be a serious security issue due to the browser's support for WebRTC.[75]
On September 12, 2016, it was reported that starting with Chrome 56, users will be warned when they visit non-secure HTTP websites to encourage more sites to make the transition to HTTPS.[76]
Security vulnerabilities
No security vulnerabilities in Chrome were exploited in the three years of Pwn2Own from 2009–2011.[77]
At Pwn2Own 2012, Chrome was defeated by a French team who used zero day exploits in the version of Flash shipped with Chrome to take complete control of a fully patched 64-bit Windows 7 PC using a booby-trapped website that overcame Chrome's sandboxing.[78]
Chrome was compromised twice at the 2012 CanSecWest Pwnium.[78][79][80] Google's official response to the exploits was delivered by Jason Kersey, who congratulated the researchers, noting "We also believe that both submissions are works of art and deserve wider sharing and recognition."[81] Fixes for these vulnerabilities were deployed within 10 hours of the submission.[82][83]
A significant number of security vulnerabilities in Chrome occur in the Adobe Flash Player. For example, the 2016 Pwn2Own successful attack on Chrome relied on four security vulnerabilities. Two of the vulnerabilities were in Flash, one was in Chrome, and one was in the Windows kernel.[84] In 2016, Google announced that it was planning to phase out Flash Player in Chrome, starting in version 53. The first phase of the plan is to disable Flash for ads and "background analytics", with the ultimate goal of disabling it completely by the end of the year, except on specific sites that Google has deemed to be broken without it. Flash would then be re-enabled with the exclusion of ads and background analytics on a site-by-site basis.[85]
Leaked documents published by WikiLeaks, codenamed Vault 7 and dated from 2013–2016, detail the capabilities of the CIA, such as the ability to compromise web browsers (including Google Chrome).[86][87]
Malware blocking and ad blocking
Google introduced download scanning protection in Chrome 17.[88] In February 2018, Google introduced an ad blocking feature based on recommendations from the Interactive Advertising Bureau. Sites that employ invasive ads are given a 30-day warning, after which their ads will be blocked.[89]Consumer Reports recommended users install dedicated ad-blocking tools instead, which offer increased security against malware and tracking.[90]
Plugins
- Chrome supported, up to version 45, plug-ins with the Netscape Plugin Application Programming Interface (NPAPI),[91] so that plug-ins (for example Adobe Flash Player) run as unrestricted separate processes outside the browser and cannot be sandboxed as tabs are. ActiveX is not supported.[91] Since 2010, Adobe Flash has been integral to Chrome and does not need be installed separately. Flash is kept up to date as part of Chrome's own updates.[92]Java applet support was available in Chrome with Java 6 update 12 and above.[93] Support for Java under OS X was provided by a Java Update released on May 18, 2010.[94]
- On August 12, 2009, Google introduced a replacement for NPAPI that is more portable and more secure[95] called Pepper Plugin API (PPAPI).[96] The default bundled PPAPI Flash Player (or Pepper-based Flash Player) was available on Chrome OS first, then replaced the NPAPI Flash Player on Linux from Chrome version 20, on Windows from version 21 (which also reduced Flash crashes by 20%),[97] and eventually came to OS X at version 23.[98]
- On September 23, 2013, Google announced that it will be deprecating and then removing NPAPI support. NPAPI support was removed from Linux in Chrome release 35.[99] NPAPI plugins like Java can no longer work in Chrome (but there are workarounds for Flash by using PPAPI Flash Player on Linux including for Chromium).[100]
- On April 14, 2015, Google released Chrome v42, disabling the NPAPI by default. This makes plugins that do not have a PPAPI plugin counterpart incompatible with Chrome, such as Java, Silverlight and Unity. However, NPAPI support could be enabled through the chrome://flags[permanent dead link] menu, until the release of version 45 in September 2015, that removed NPAPI support entirely.[101]
Privacy
Incognito mode

Google Chrome Incognito mode message
The private browsing feature called Incognito mode prevents the browser from permanently storing any history information, cookies, site data, or form inputs[102]. Downloaded files and bookmarks will be stored. In addition, user activity is not hidden from visited websites or the internet service provider.
Incognito mode is similar to the private browsing feature in other web browsers. It doesn't prevent saving in all windows: "You can switch between an incognito window and any regular windows you have open. You'll only be in incognito mode when you're using the incognito window".[103]
Listening capabilities
On June 2015 the Debian developer community discovered that Chromium 43 and Chrome 43 were programmed to download the Hotword Shared Module, which could enable the OK Google voice recognition extension, although by default it was "off". This raised privacy concerns in the media.[104][105] The module was removed in Chrome 45, which was released on 1 September 2015, and was only present in Chrome 43 and 44.[106][107]
User tracking concerns
Chrome sends details about its users and their activities to Google through both optional and non-optional user tracking mechanisms.[108][109]
Some of the tracking mechanisms can be optionally enabled and disabled through the installation interface[110] and through the browser's options dialog.[111] Unofficial builds, such as SRWare Iron, seek to remove these features from the browser altogether.[112] The RLZ feature is not included in the Chromium browser either.[113]
In March 2010, Google devised a new method to collect installation statistics: the unique ID token included with Chrome is now only used for the first connection that Google Update makes to its server.[114]
The optional suggestion service included in Google Chrome has been criticized because it provides the information typed into the Omnibox to the search provider before the user even hits return. This allows the search engine to provide URL suggestions, but also provides them with web usage information tied to an IP address.[115]
The optional feature to use a web service to help resolve spelling errors has privacy implications.[116]
| Method[112] | Information sent | When | Optional? | Opt-in? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Installation | Randomly generated token included in installer. Used to measure success rate of Google Chrome once at installation.[117] | On installation | No | N/A |
RLZ identifier[118] | Encoded string, according to Google, contains non-identifying information about where Chrome was downloaded from and its installation week, and is used to measure promotional campaigns.[117] Google provides the source code to decode this string.[113] RLZ can be disabled in the Chrome Operating System.[117] For Chrome browsers running in all other operating systems:[117]
|
| Partial [note 2][117] | No |
clientID[111] | Unique identifier along with user preferences, logs of usage metrics and crashes. | Unknown | Yes[119] | Yes |
Omnibox predictions[111] | Text typed into the address bar. | While typing | Yes | No |
Page not found | Text typed into the address bar. | Upon receiving "Server not found" response | Yes | No |
Google Update | Information about how often Chrome is used, details about the OS and Chrome version. | Periodically | Partial [note 3][120] | No |
Do Not Track
In February 2012, Google announced that Chrome would implement the Do Not Track (DNT) standard to inform websites the user's desire to be not tracked. The protocol was implemented in version 23. In line with the W3's draft standard for DNT,[121] it is turned off by default in Chrome.[122]
Speed
The JavaScript virtual machine used by Chrome, the V8 JavaScript engine, has features such as dynamic code generation, hidden class transitions, and precise garbage collection.[29]
In 2008, several websites performed benchmark tests using the SunSpider JavaScript Benchmark tool as well as Google's own set of computationally intense benchmarks, which include ray tracing and constraint solving.[123] They unanimously reported that Chrome performed much faster than all competitors against which it had been tested, including Safari (for Windows), Firefox 3.0, Internet Explorer 7, Opera, and Internet Explorer 8.[124][125][126][57][127][128] However, on October 11, 2010, independent tests of JavaScript performance, Chrome has been scoring just behind Opera's Presto engine since it was updated in version 10.5.[129]
On September 3, 2008, Mozilla responded by stating that their own TraceMonkey JavaScript engine (then in beta), was faster than Chrome's V8 engine in some tests.[130][131][132]John Resig, Mozilla's JavaScript evangelist, further commented on the performance of different browsers on Google's own suite, commenting on Chrome's "decimating" of the other browsers, but he questioned whether Google's suite was representative of real programs. He stated that Firefox 3.0 performed poorly on recursion-intensive benchmarks, such as those of Google, because the Mozilla team had not implemented recursion-tracing yet.[133]
Two weeks after Chrome's launch in 2008, the WebKit team announced a new JavaScript engine, SquirrelFish Extreme,[134] citing a 36% speed improvement over Chrome's V8 engine.[135][136][137]
Like most major web browsers, Chrome uses DNS prefetching to speed up website lookups,[138] as do other browsers like Firefox,[139] Safari,[140] Internet Explorer (called DNS Pre-resolution),[141] and in Opera as a UserScript (not built-in).[142]
Chrome formerly used their now deprecated SPDY protocol instead of only HTTP[143][144] when communicating with servers that support it, such as Google services, Facebook, Twitter. SPDY support was removed in Chrome version 51.
Stability

Screenshot of Chrome browser crash
A multi-process architecture is implemented in Chrome[145] where, by default, a separate process is allocated to each site instance and plugin. This procedure is termed process isolation,[146] and it prevents tasks from interfering with each other, raising security and stability. An attacker successfully gaining access to one application gains access to no others,[147] and failure in one instance results in a Sad Tab screen of death, similar to the well-known Sad Mac, but only one tab crashes instead of the whole application. This strategy exacts a fixed per-process cost up front, but results in less memory bloat over time as fragmentation is confined to each instance and no longer needs further memory allocations.[29] This architecture was adopted in Safari[148] and Firefox.[149]
Chrome includes a process management utility called Task Manager which lets users see what sites and plugins are using the most memory, downloading the most bytes and overusing the CPU and provides the ability to terminate them.[29] Chrome Version 23 ensures its users an improved battery life for the systems supporting Chrome's GPU accelerated video decoding.[150][51]
User interface
@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;max-width:none!important.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center

By default, the main user interface includes back, forward, refresh/cancel and menu buttons. A home button is not shown by default, but can be added through the Settings page to take the user to the new tab page or a custom home page.[151]
Tabs are the main component of Chrome's user interface and have been moved to the top of the window rather than below the controls. This subtle change contrasts with many existing tabbed browsers which are based on windows and contain tabs. Tabs, with their state, can be transferred seamlessly between window containers by dragging. Each tab has its own set of controls, including the Omnibox.[29]
The Omnibox is a URL box that combines the functions of both the address bar and search box. If a user enters the URL of a site previously searched from, Chrome allows pressing Tab to search the site again directly from the Omnibox. When a user starts typing in the Omnibox, Chrome provides suggestions for previously visited sites (based on the URL or in-page text), popular websites (not necessarily visited before – powered by Google Instant), and popular searches. Although Instant can be turned off, suggestions based on previously visited sites cannot be turned off. Chrome will also autocomplete the URLs of sites visited often.[29] If a user types keywords into the Omnibox that don't match any previously visited websites and presses enter, Chrome will conduct the search using the default search engine.
One of Chrome's differentiating features is the New Tab Page, which can replace the browser home page and is displayed when a new tab is created. Originally, this showed thumbnails of the nine most visited web sites, along with frequent searches, recent bookmarks, and recently closed tabs; similar to Internet Explorer and Firefox with Google Toolbar, or Opera's Speed Dial.[29] In Google Chrome 2.0, the New Tab Page was updated to allow users to hide thumbnails they did not want to appear.[152]
Starting in version 3.0, the New Tab Page was revamped to display thumbnails of the eight most visited web sites. The thumbnails could be rearranged, pinned, and removed. Alternatively, a list of text links could be displayed instead of thumbnails. It also features a "Recently closed" bar that shows recently closed tabs and a "tips" section that displays hints and tricks for using the browser.[153]
Chrome includes a bookmarks submenu that lists the user's bookmarks, provides easy access to Chrome's Bookmark Manager, and allows the user to toggle a bookmarks bar on or off.
For web developers, Chrome features an element inspector (Inspect Element), similar to the browser extension in Firebug, which allows users to look into the DOM and see what makes up the webpage.[138]
Chrome has special URLs that load application-specific pages instead of websites or files on disk. Chrome also has a built-in ability to enable experimental features. Originally called about:labs, the address was changed to about:flags to make it less obvious to casual users.[154][155]
In March 2011, Google introduced a new simplified logo to replace the previous 3D logo that had been used since the project's inception. Google designer Steve Rura explained the company reasoning for the change: "Since Chrome is all about making your web experience as easy and clutter-free as possible, we refreshed the Chrome icon to better represent these sentiments. A simpler icon embodies the Chrome spirit – to make the web quicker, lighter, and easier for all."[156]
In September 2013, Google started making Chrome apps "For your desktop." This meant offline access, desktop shortcuts, and less dependence on Chrome- They launch in a window separate from Chrome, and look more like native applications.[157]
Desktop shortcuts and apps
Chrome allows users to make local desktop shortcuts that open web applications in the browser. The browser, when opened in this way, contains none of the regular interface except for the title bar, so as not to "interrupt anything the user is trying to do". This allows web applications to run alongside local software (similar to Mozilla Prism and Fluid).[29]
This feature, according to Google, will be enhanced with the Chrome Web Store, a one-stop web-based web applications directory which opened in December 2010.[158][159]
Chrome Web Store
Announced on December 7, 2010, the Chrome Web Store allows users to install web applications as extensions to the browser, although most of these extensions function simply as links to popular web pages and/or games, but some of the apps like Springpad do provide extra features like offline access. The themes and extensions have also been tightly integrated into the new store, allowing users to search the entire catalog of Chrome extras.[160]
The Chrome Web Store was opened on February 11, 2011, with the release of Google Chrome 9.0.[161]
Extensions
Google Chrome Extensions are browser extensions that modify Google Chrome.[162] These extensions are written using web technologies like HTML, JavaScript, and CSS.[163] They are distributed through Chrome Web Store[164] (formerly Google Chrome Extensions Gallery).[162] All users with a Google Account are able to add extensions after developing them.[165] Many Chrome extensions, once installed, have access to the user's data. There are three levels of permissions that an app or extension may request.[166]
On September 9, 2009, Google enabled extensions by default on Chrome's developer channel, and provided several sample extensions for testing.[167] In December, the Google Chrome Extensions Gallery beta began with approximately 300 extensions.[44][168] It was launched on January 25, 2010 along with Google Chrome 4.0, containing approximately 1500 extensions.[169]
On May 27, 2014, Google issued an update to Chrome preventing Windows users from installing extensions obtained outside the Chrome Web Store.[170]
Notable examples
Adblock Plus[171]- Adblock for Chrome
- Cut the Rope
- Dropbox
- Evernote Web
Facebook Messenger[172]- Ghostery
- Googlepedia
- Google Maps
- HTTPS Everywhere
- Pandora Radio
- Pixlr Express
- Privacy Badger
Streamus (discontinued)- Turn Off the Lights
- TweetDeck
- Stop Tony Meow
Themes
Starting with Google Chrome 3.0, users can install themes to alter the appearance of the browser.[173] Many free third-party themes are provided in an online gallery,[174] accessible through a "Get themes" button in Chrome's options.[175]
Automatic web page translation
Starting with Google Chrome 4.1 the application added a built-in translation bar using Google Translate. Translation is currently available for 52 languages.[176] When Chrome detects a foreign language other than the user's preferred language as set during the installation time, it asks the user whether or not to translate.
Release channels, cycles and updates
The first production release on December 11, 2008, marked the end of the initial Beta test period and the beginning of Production. Shortly thereafter, on January 8, 2009, Google announced an updated release system with three channels: Stable (corresponding to the traditional Production), Beta, and Developer preview (also called the "Dev" channel). Where there were before only two channels: Beta and Developer, now there were three. Concurrently, all Developer channel users were moved to the Beta channel along with the promoted Developer release. Google explained that now the Developer channel builds would be less stable and polished than those from the initial Google Chrome's Beta period. Beta users could opt back to the Developer channel as desired.
Each channel has its own release cycle and stability level. The Stable channel updated roughly quarterly, with features and fixes that passed "thorough" testing in the Beta channel. Beta updated roughly monthly, with "stable and complete" features migrated from the Developer channel. The Developer channel updated once or twice per week and was where ideas and features were first publicly exposed "(and sometimes fail) and can be very unstable at times". [Quoted remarks from Google's policy announcements.][177][178][179]

Google Chrome Canary Application Icon
On July 22, 2010, Google announced it would ramp up the speed at which it releases new stable versions; the release cycles were shortened from quarterly to six weeks for major Stable updates.[180] Beta channel releases now come roughly at the same rate as Stable releases, though approximately one month in advance, while Dev channel releases appear roughly once or twice weekly, allowing time for basic release-critical testing.[181] This faster release cycle also brought a fourth channel: the "Canary" channel, updated daily from a build produced at 09:00 UTC from the most stable of the last 40 revisions.[182] The name refers to the practice of using canaries in coal mines, so if a change "kills" Chrome Canary, it will be blocked from migrating down to the Developer channel, at least until fixed in a subsequent Canary build.[183] Canary is "the most bleeding-edge official version of Chrome and somewhat of a mix between Chrome dev and the Chromium snapshot builds". Canary releases run side-by-side with any other channel; it is not linked to the other Google Chrome installation and can therefore run different synchronization profiles, themes, and browser preferences. This ensures that fallback functionality remains even when some Canary update may contain release-breaking bugs.[184] It does not natively include the option to be the default browser, although on Windows and OS X it can be set through System Preferences. Canary was Windows-only at first; an OS X version was released on May 3, 2011.[185]
The Chrome beta channel for Android was launched on January 10, 2013; like Canary, it runs side-by-side with the stable channel for Android.[186][187] Chrome Dev for Android was launched on April 29, 2015.[188]
All Chrome channels are automatically distributed according to their respective release cycles. The mechanism differs by platform. On Windows, it uses Google Update, and auto-update can be controlled via Group Policy.[189] Alternatively, users may download a standalone installer of a version of Chrome that does not auto-update.[190][191] On OS X, it uses Google Update Service, and auto-update can be controlled via the OS X "defaults" system.[192] On Linux, it lets the system's normal package management system supply the updates. This auto-updating behavior is a key difference from Chromium, the non-branded open source browser which forms the core of Google Chrome. Because Chromium also serves as the pre-release development trunk for Chrome, its revisions are provided as source code and buildable snapshots are produced continuously with each new commit, requiring users to manage their own browser updates.[193]
Release version numbers
Releases are identified by a four-part version number, e.g. 42.0.2311.90 (Windows Stable release April 14, 2015[194]). The components are major.minor.build.patch.[195][196]
Major.minor reflects scheduling policy
Build.patch identifies content progression
Major represents a product release. These are scheduled 7–8 per year, unlike other software systems where the major version number updates only with substantial new content.
Minor is usually 0. References to version 'x' or 'x.0', e.g. 42.0, refer to this major.minor designation.
Build is ever increasing. For a release cycle, e.g. 42.0, there are several builds in the Canary and Developer period. The last build number from Developer is kept throughout Beta and Stable and is locked with the major.minor for that release.
Patch resets with each build, incrementing with each patch. The first patch is 0, but usually the first publicly released patch is somewhat higher. In Beta and Stable, only patch increments.
Chromium and Chrome release schedules are linked through Chromium
(Major) version Branch Point dates, published annually.[195] The Branch Points precede the final Chrome Developer build (initial) release by 4 days (nearly always) and the Chrome Stable initial release by roughly 53 days.[197]
Example: The version 42 Branch Point was February 20, 2015.[195] Developer builds stopped advancing at build 2311 with release 42.0.2311.4 on February 24,[198] 4 days later. The first Stable release, 42.0.2311.90, was April 14, 2015,[194] 53 days after the Branch Point.
Color management
Chrome supports color management by using the system-provided ICC v2 and v4 support on macOS, and from version 22 supports ICC v2 profiles by default on other platforms.[199]
T-Rex
In Chrome, when not connected to the Internet and an error message displaying "There is no Internet" is shown, on the top, an "8-bit" Tyrannosaurus rex is shown, but when pressing the space bar on a keyboard, mouse-clicking on it or tapping it on touch devices, the T-Rex instantly jumps once and dashes across a cactus-ridden desert, revealing it to be an Easter egg in the form of a platform game.[200][201][202][203] The game itself is an infinite runner, and there is no time limit in the game as it progresses faster and periodically tints to a black background. A school Chromebook administrator can disable the game.[204]
Platforms
Chrome runs on:
Windows 7 or later[205]
OS X 10.10 or later[205]
64-bit versions of Ubuntu 14.04+, Debian 8+, openSUSE 13.3+ and Fedora 24+[205]
Android 4.1 or later
iOS 10 or later
As of April 2016[update], stable 32-bit and 64-bit builds are available for Windows, with only 64-bit stable builds available for Linux and macOS.[206][207][208] 64-bit Windows builds became available in the developer channel and as canary builds on June 3, 2014,[209] in beta channel on July 30, 2014,[210] and in stable channel on August 26, 2014.[211] 64-bit OS X builds became available as canary builds on November 7, 2013,[212][213] in beta channel on October 9, 2014,[214] and in stable channel on November 18, 2014.[206]
Compatibility
Operating system | Latest version | Support status | |
|---|---|---|---|
Windows | 7 and later | 69 | 2009– |
XP and Vista | 49 | 2008–2016 | |
macOS | 10.10 and later | 69 | 2014– |
10.9 | 65 | 2013–2018 | |
10.6–10.8 (x64) | 49 | 2010–2016 | |
10.6 (IA-32) | 38 | 2010–2014 | |
10.5 | 21 | 2010–2012 | |
Linux desktop | x64 | 69 | 2010– |
| IA-32 | 48 | 2010–2016 | |
Android | 4.1 and later | 69 | 2012– |
4.0 | 42 | 2012–2015 | |
iOS | 10.0 and later | 69 | 2016– |
9.x | 63 | 2015–2018 | |
Android
A beta version for Android 4.0 devices was launched on February 7, 2012, available for a limited number of countries from Google Play.[215]
Notable features: synchronization with desktop Chrome to provide the same bookmarks and view the same browser tabs,[216] page pre-rendering,[217] hardware acceleration.[218]
Many of the latest HTML5 features: almost all of the Web Platform's features: GPU-accelerated canvas, including CSS 3D Transforms, CSS animations, SVG, WebSocket (including binary messages), Dedicated Workers; it has overflow scroll support, strong HTML5 video support, and new capabilities such as IndexedDB, WebWorkers, Application Cache and the File APIs, date- and time-pickers, parts of the Media Capture API.[217][219] Also supports mobile oriented features such as Device Orientation and Geolocation.[219]
Mobile customizations: swipe gesture tab switching,[216] link preview allows zooming in on (multiple) links to ensure the desired one is clicked,[216] font size boosting to ensure readability regardless of the zoom level.[219]
Features missing in the mobile version include sandboxed tabs,[217][220] Safe Browsing,[217] apps or extensions,[218] Adobe Flash (now and in future),[218]Native Client.[218]
Development changes: remote debugging,[217][221] part of the browser layer has been implemented in Java, communicating with the rest of the Chromium and WebKit code through Java Native Bindings.[219] The code of Chrome for Android is a fork of the Chromium project. It is a priority to upstream most new and modified code to Chromium and WebKit to resolve the fork.[219]
The April 17, 2012 update, included the availability to access in 31 additional languages and in all countries where Google Play is available. A desktop version of a website can also be requested as opposed to a mobile version. In addition, Android users can now add bookmarks to their Android home screens if they choose and decide which apps should handle links opened in Chrome.[222]
On June 27, 2012, Google Chrome for Android exited beta and became stable.[223]
Chrome 18.0.1026311, released on September 26, 2012, was the first version of Chrome for Android to support mobile devices based on Intel x86.[224]
Starting from version 25, the Chrome version for Android is aligned with the desktop version, and usually new stable releases are available at the same time between the Android and the desktop version. Google released a separate Chrome for Android beta channel on January 10, 2013, with version 25.[186] As of 2013[update] a separate beta version of Chrome is available in the Google Play store – it can run side-by-side with the stable release.[225]
Chrome OS
Google Chrome is the basis of Google's Chrome OS operating system that ships on specific hardware from Google's manufacturing partners.[226] The user interface has a minimalist design resembling the Google Chrome browser. Chrome OS is aimed at users who spend most of their computer time on the Web; the only applications on the devices are a browser incorporating a media player and a file manager.[227][228][229][230][231]
Google announced Chrome OS on July 7, 2009.[232]
iOS
Chrome is available on Apple's mobile iOS operating system as Google Chrome for iOS. Released in the Apple App Store on June 26, 2012, it supports the iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch, and requires that the device has iOS 10.0 or greater installed.[233] In accordance with Apple's requirements for browsers released through their App Store, this version of Chrome uses the iOS WebKit – which is Apple's own mobile rendering engine and components, developed for their Safari browser – therefore it is restricted from using Google's own V8 JavaScript engine.[234][235] Chrome is the default web browser for the iOS Gmail application, but it cannot be used as the device-wide default application for opening webpages because Apple has not provided iOS users with the option to change the default from Safari.[236]
In a review by Chitika, Chrome was noted as having 1.5% of the iOS web browser market as of July 18, 2012.[237] In October 2013, Chrome had 3% of the iOS browser market.[238]
Linux
On Linux distributions, support for 32-bit Intel processors ended in March 2016 although Chromium is still supported .[239] As of Chrome version 26, Linux installations of the browser may be updated only on systems that support GCC v4.6 and GTK v2.24 or later. Thus deprecated systems include (for example) Debian 6's 2.20, and RHEL 6's 2.18.[240]
Windows
Support for Google Chrome on Windows XP and Windows Vista ended in April 2016.[241] The last release of Google Chrome that can be run on Windows XP and Windows Vista was version 49.0.2623.112 m,[242] released on April 7, 2016,[243] then re-released on April 11, 2016.[244]
"Windows 8 mode" was introduced in 2012 and has since been discontinued. It was provided to developer channel, which enabled Windows 8 and 8.1 users to run Chrome with a full-screen, tablet-optimized interface, with access to snapping, sharing, and search functionalities.[245] In October 2013, Windows 8 mode on developer channel changed to use a desktop environment mimicking the interface of Chrome OS with a dedicated windowing system and taskbar for web apps.[246] This was discontinued as of version 49 and users that have upgraded to Windows 10 will lose this feature.[247]
macOS
Google dropped support for Mac OS X 10.5 with the release of Chrome 21.[248] Support for 32-bit versions of Chrome ended in October 2014 with the release of Chrome 39.[249][250][206] Support for Mac OS X 10.6, 10.7, and 10.8 ended in April 2016 with the release of Chrome 50. Support for OS X 10.9 ended in July 2018 with the release of Chrome 68.[citation needed]
Reception
Google Chrome was met with acclaim upon release. In 2008, Matthew Moore of The Daily Telegraph summarized the verdict of early reviewers: "Google Chrome is attractive, fast and has some impressive new features..."[251]
Initially, Microsoft reportedly played down the threat from Chrome and predicted that most people would embrace Internet Explorer 8. Opera Software said that "Chrome will strengthen the Web as the biggest application platform in the world".[252] But by February 25, 2010, BusinessWeek had reported that "For the first time in years, energy and resources are being poured into browsers, the ubiquitous programs for accessing content on the Web. Credit for this trend – a boon to consumers – goes to two parties. The first is Google, whose big plans for the Chrome browser have shaken Microsoft out of its competitive torpor and forced the software giant to pay fresh attention to its own browser, Internet Explorer. Microsoft all but ceased efforts to enhance IE after it triumphed in the last browser war, sending Netscape to its doom. Now it's back in gear."[253] Mozilla said that Chrome's introduction into the web browser market comes as "no real surprise", that "Chrome is not aimed at competing with Firefox", and furthermore that it would not affect Google's revenue relationship with Mozilla.[254][255]
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
Chrome's design bridges the gap between desktop and so-called "cloud computing." At the touch of a button, Chrome lets you make a desktop, Start menu, or QuickLaunch shortcut to any Web page or Web application, blurring the line between what's online and what's inside your PC. For example, I created a desktop shortcut for Google Maps. When you create a shortcut for a Web application, Chrome strips away all of the toolbars and tabs from the window, leaving you with something that feels much more like a desktop application than like a Web application or page.
— PC World[256]
Usage
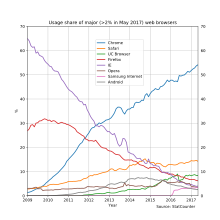
Usage share of web browsers according to StatCounter[257]

Browser Market Share Worldwide July 2017[258]
Google Chrome (59.69%)
Safari (13.85%)
UC Browser (7.03%)
Firefox (5.02%)
Opera (3.35%)
Internet Explorer (3.01%)
No info (8.05%)
Chrome overtook Firefox in November 2011, in worldwide usage. As of June 2016[update], according to StatCounter, Google Chrome had 62% worldwide desktop usage share, making it the most widely used web browser, while Firefox had 16% and Internet Explorer had 12%.[259][260]
Along with Safari and Mozilla Firefox, Chrome receives a weekend "bump", which boosts its market share by as much as three percentage points on week-ends, at the expense of Internet Explorer.[261]
It was reported by StatCounter, a web analytics company, that for the single day of Sunday, March 18, 2012, Chrome was the most used web browser in the world for the first time. Chrome secured 32.7% of the global web browsing on that day, while Internet Explorer followed closely behind with 32.5%.[262]
From May 14–21, 2012, Google Chrome was for the first time responsible for more Internet traffic than Microsoft's Internet Explorer, which long had held its spot as the most used web browser in the world.[263] According to StatCounter, 31.88% of web traffic was generated by Chrome for a sustained period of one week and 31.47% by Internet Explorer. Though Chrome had topped Internet Explorer for single day's usage in the past, this was the first time it had led for one full week.[264]
At the 2012 Google I/O developers' conference, Google claimed that there were 310 million active users of Chrome, almost double the number in 2011, which was stated as 160 million active users.[265]
In June 2013, according to StatCounter, Chrome overtook Internet Explorer for the first time in the US.[266]
In August 2013, Chrome was used by 43% of internet users worldwide. This study was done by Statista, which also noted that in North America, 36% of people use Chrome, the lowest in the world.[267]
As of February 2018[update], Chrome is the most used browser in virtually all countries, with most exceptions in Africa.[23]
Enterprise deployment
In December 2010, Google announced that to make it easier for businesses to use Chrome they would provide an official Chrome MSI package. For business use it is helpful to have full-fledged MSI packages that can be customized via transform files (.mst) – but the MSI provided with Chrome is only a very limited MSI wrapper fitted around the normal installer, and many businesses find that this arrangement does not meet their needs.[269] The normal downloaded Chrome installer puts the browser in the user's local app data directory and provides invisible background updates, but the MSI package will allow installation at the system level, providing system administrators control over the update process[270] – it was formerly possible only when Chrome was installed using Google Pack. Google also created group policy objects to fine tune the behavior of Chrome in the business environment, for example by setting automatic updates interval, disabling auto-updates, and configuring a home page.[271] Until version 24 the software is known not to be ready for enterprise deployments with roaming profiles or Terminal Server/Citrix environments.[272]
Chromium
In September 2008, Google released a large portion of Chrome's source code as an open-source project called Chromium. This move enabled third-party developers to study the underlying source code and to help port the browser to the macOS and Linux operating systems. The Google-authored portion of Chromium is released under the permissive BSD license.[273] Other portions of the source code are subject to a variety of open-source licenses.[274] Chromium is similar to Chrome, but lacks built-in automatic updates and built-in Flash player, as well as Google branding and has a blue-colored logo instead of the multicolored Google logo.[275][276] Chromium does not implement user RLZ tracking.[113][108][277] Initially, the Google Chrome PDF viewer, PDFium, was excluded from Chromium, but was later made open-source in May 2014.[278][279] PDFium can be used to fill PDF forms.[280]
Developing for Chrome
It is possible to develop applications, extensions, and themes for Chrome. They are zipped in a .crx file and contain a manifest file that specifies basic information (such as version, name, description, privileges, etc.), and other files for the user interface (icons, popups, etc.). Google has an official developer's guide.[281] Chrome has its own web store where users and developers can upload and download these applications and extensions.[282]
See also
- Google Apps for Work
- Google Chrome Experiments
- Google Chrome Frame
- History of web browsers
- List of web browsers
Notes
^ Chrome's WebKit & Blink layout engines and its V8 JavaScript engine are each free and open-source software, while its other components are each either open-source or proprietary. However, section 9 of Google Chrome's Terms of Service designates the whole package as proprietary freeware.
^ RLZ can be disabled in the Chrome Operating System, and is not in Chrome browsers downloaded to a desktop directly from Google.com/chrome. No way to disable in phones, tablets and possibly laptops.
^ Requires advanced user intervention.
References
^ "Stable Channel Update for Desktop". Chrome Releases. Blogger. September 4, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
^ "Chrome for Android Update". Chrome Releases blog. Blogger. September 4, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
^ "Google Chrome on the App Store". iTunes Preview. September 4, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
^ "Beta Channel Update for Desktop". Google Blogspot. September 4, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
^ "Chrome Beta for Android Update". Google Blogspot. September 1, 2018. Retrieved September 3, 2018.
^ abcde "Google Chrome". OmahaProxy CSV Viewer. Chromium team.
^ "Dev Channel Update for Desktop". Google Blogspot. August 28, 2018. Retrieved August 28, 2018.
^ "Chromium (Google Chrome)". Ohloh.net. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
^ "Chromium coding style". Google Open Source. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
^ Lextrait, Vincent (January 2010). "The Programming Languages Beacon, v10.0". Archived from the original on May 30, 2012. Retrieved March 14, 2010.
^ "Chrome for iOS".
^ "Supported languages". Google Play Console Help. Retrieved December 18, 2015.
^ abcd "Google Chrome Terms of Service".
^ Paul, Ryan (September 2, 2008). "Google unveils Chrome source code and Linux port". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Welcome to Chromium". blog.chromium.org.
^ "Explaining Why We Don't Endorse Other Systems". gnu.org. Retrieved 2018-04-07.The central part of Chrome OS is the nonfree Chrome browser.
^ LaForge, Anthony (August 9, 2016). "Flash and Chrome". The Keyword Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ ab Bright, Peter (April 3, 2013). "Google going its own way, forking WebKit rendering engine". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Protalinski, Emil (April 8, 2013). "It's here: Google replaces WebKit version ID with Blink in latest Chrome build". The Next Web. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Hello Blink". Bruce Lawson's Blog. Retrieved April 3, 2013.
^ Statcounter. "Desktop Browser Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats". gs.statcounter.com. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
^ Statcounter. "Browser Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats". gs.statcounter.com. Retrieved February 9, 2018.
^ ab "Browser Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats". StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved March 7, 2018.
^ Julia Angwin (July 9, 2009). "Sun Valley: Schmidt Didn't Want to Build Chrome Initially, He Says". WSJ Digits Blog. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
^ "Rumours surround Google browser".
^ Scott McCloud (September 1, 2008). "Surprise!". Google Blogoscoped. Retrieved September 1, 2008.
^ Philipp Lenssen (September 1, 2008). "Google Chrome, Google's Browser Project". Retrieved September 1, 2008.
^ Philipp Lenssen (September 1, 2008). "Google on Google Chrome – comic book". Google Blogoscoped. Retrieved September 1, 2008.
^ abcdefghijk "Google Chrome comic". Google Book Search. September 1, 2008. Retrieved September 2, 2008.
^ ab Pichai, Sundar; Upson, Linus (September 1, 2008). "A fresh take on the browser". Official Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Dougerty, Conor (July 12, 2015). "Sundar Pichai of Google Talks About Phone Intrusion". New York Times. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
^ "Google Chrome - The reason behind its name revealed!". The Windows Club. Retrieved September 3, 2015.
^ "It was when not if... Google Chrome". September 2008. Archived from the original on December 8, 2016. Retrieved June 21, 2017. CS1 maint: Unfit url (link)
^ Fried, Ina (October 7, 2008). "Be sure to read Chrome's fine print". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Google Terms of Service – Policies & Principles – Google". Google.com. March 1, 2012. Retrieved March 30, 2013.
^ Needleman, Rafe (September 2, 2008). "Google Chrome update: First screenshot, and live-blog alert". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Google launches Chrome web browser". The Canadian Press. Associated Press. September 2, 2008. Retrieved September 2, 2008.
^ "Come on Google... Chrome for Mac?". November 2008. Retrieved November 22, 2008.
^ Gruener, Wolfgang (January 3, 2009). "Google Chrome crosses 1% market share again". Chicago (IL), United States: TG Daily. Archived from the original on March 10, 2009. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ Shankland, Stephen (January 9, 2009). "Chrome gets Mac deadline, extensions foundation". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Early Access Release Channels". dev.chromium.org. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Danger: Mac and Linux builds available". Retrieved June 9, 2009.
^ Larson, Mark (December 8, 2009). "Beta Update: Linux, Mac, and Windows". Chrome Releases. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ ab Rakowski, Brian (December 8, 2009). "Google Chrome for the holidays: Mac, Linux and extensions in beta". Official Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Rakowski, Brian (May 25, 2010). "A new Chrome stable release: Welcome, Mac and Linux!". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Microsoft offers browser choices to Europeans". BBC News. March 1, 2010. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ "NPAPI deprecation: developer guide - The Chromium Projects". chromium.org. Retrieved September 3, 2015.
^ Peteris Krumins (September 5, 2008). "Code reuse in Google Chrome Browser". Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Ian Fette (February 19, 2010). "Hello HTML5". Google. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ "HTML Video Codec Support in Chrome". blog.chromium.org. January 11, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ ab Fischmann, Ami (November 6, 2012). "Longer battery life and easier website permissions". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Trollope, Rowan (December 22, 2013). "Open-Sourced H.264 Removes Barriers to WebRTC". Retrieved December 22, 2013.
^ "Google Chrome Beta arrives on Android". Engadget. AOL. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ "Chrome Out Of Beta, Default Browser Of Android 4.1".
^ Matney, Lucas. "Chrome is coming to augmented reality and Google Daydream".
^ Needleman, Rafe (June 12, 2008). "The future of the Firefox address bar". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ ab Shankland, Stephen (October 7, 2008). "Speed test: Google Chrome beats Firefox, IE, Safari". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Kevin Purdy (June 11, 2009). "Lifehacker Speed Tests: Safari 4, Chrome 2, and More – Browsers". Lifehacker. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Laforge, Anthony. "Stable Channel Update". Google. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
^ "ECMAScript test262". ECMAScript.org. Archived from the original on May 14, 2011. Retrieved May 6, 2011.
^ "CSS 2.1 Test Suite RC6 Results". W3C. Retrieved May 6, 2011.
^ "HTML5 test desktop". Visred. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ "HTML5 test desktop browser comparison". Visred. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ "HTML5 test Android Chrome 41 Galaxy S5". Visred. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ "HTML5 test tablet". Sights. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ "HTML5 test mobile". Sights. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ "HTML5test - How well does your browser support HTML5?". html5test.com. Retrieved October 29, 2015.
^ Chung, Marc (September 5, 2008). "chromes-process model explained". Archived from the original on March 21, 2009. Retrieved September 10, 2008.
^ Barth, Adam; Jackson, Collin; Reis, Charles; The Google Chrome Team. "The Security Architecture of the Chromium Browser" (PDF). Stanford Security Laboratory. Retrieved September 11, 2008.
^ Markus Gutschke (May 6, 2009). "Re: (PATCH 2/2) x86-64: seccomp: fix 32/64 syscall hole". Retrieved February 17, 2011.
^ Jake Edge (August 19, 2009). "Google's Chromium sandbox". Retrieved February 17, 2011.
^ "Issue 53 - chromium - No Master Password Option". Google. September 2, 2008. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
^ Kember, Elliott (August 7, 2013). "Chrome's Password Security Strategy Is Insane". Mashable.com. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
^ "Issue 53 - chromium - No Master Password Option (post #151)". Retrieved May 3, 2014.
^ Huge Security Flaw Leaks VPN Users’ Real IP-addresses TorrentFreak.com (January 30, 2015). Retrieved on February 21, 2015.
^ Bates, Adam. "InsightPortal | QualityTaskForce | Chrome will start flagging insecure HTTP sites". www.insightportal.io. Retrieved August 8, 2017.
^ Gregg Keizer (March 10, 2011). "Google's Chrome untouched at Pwn2Own hack match". Computerworld.
^ ab "Pwn2Own 2012: Google Chrome browser sandbox first to fall". ZDNet. CBS Interactive. March 7, 2012. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "CanSecWest Pwnium: Google Chrome hacked with sandbox bypass". ZDNet. CBS Interactive. March 7, 2012. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Teenager hacks Google Chrome with three 0day vulnerabilities". ZDNet. CBS Interactive. March 9, 2012. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Kersey, Jason (March 10, 2012). "Chrome Stable Update". Retrieved March 10, 2012.
^ Goodin, Dan (October 10, 2012). "Google Chrome exploit fetches "Pinkie Pie" $60,000 hacking prize". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Pwnium 2: results and wrap-up". Chromium Blog. October 10, 2012.
^ "Pwn2own Day 1 Exploits: Google Chrome, Adobe Flash, Apple Safari". Retrieved September 20, 2016.
^ "Google targets HTML5 default for Chrome instead of Flash in Q4 2016". VentureBeat. Retrieved September 20, 2016.
^ "WikiLeaks posts trove of CIA documents detailing mass hacking". CBS News. 2017-03-07.
^ Greenberg, Andy (2017-03-07). "How the CIA Can Hack Your Phone, PC, and TV (Says WikiLeaks)". WIRED.
^ "Chrome Browser". Google.com. Retrieved April 21, 2014.
^ Tsukayama, Hayley (February 15, 2018). "Google's Chrome ad blocker means the Web's largest ad company is also now advertising's biggest traffic cop". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 15, 2018.
^ Chaikivsky, Andrew (February 15, 2018). "Want to Protect Against Websites That Spy on You? Get an Ad Blocker". Consumer Reports. Retrieved February 15, 2018.
^ ab "Google Chrome FAQ for web developers". Google. Archived from the original on September 4, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Paul, Ryan (March 2010). "Google bakes Flash into Chrome, hopes to improve plug-in API". Retrieved March 14, 2010.
^ "Java and Google Chrome". java.com. Retrieved December 11, 2009.
^ "Issue 10812 – chromium – No java plugin support yet". Google. Retrieved May 18, 2010.
^ "Pepper.wiki". Code.google.com. February 24, 2012. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
^ "Pepper Plugin API (PPAPI)". Chromium.org. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
^ "Chromium Blog: The road to safer, more stable, and flashier Flash". blog.chromium.org. August 8, 2012. Retrieved August 29, 2012.
^ "Securing Flash Player for our Mac users". Google. Retrieved November 14, 2012.
^ "Chromium Blog: Saying Goodbye to Our Old Friend NPAPI". Chromium Blog. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
^ "PSA: Chrome for Linux planning to drop NPAPI support as soon as April". Retrieved April 22, 2015.Another thing I found last night is a Debian package called PepperFlashPlayer. Apparently it works the same way as the existing FlashPlayer package (which downloads Adobe Flash from Adobe and installs it) -- it downloads Chrome from Google, extracts the PPAPI Flash plugin, and installs it for Chromium. That might be a good work-around for Chromium users in the interim. (Note: I am not endorsing this method, just making people aware of it.) But obviously it would be better if PPAPI Flash were available in a more "official" context.
^ "NPAPI deprecation: developer guide". www.chromium.org.
^ "Browse in private - Computer - Google Chrome Help". support.google.com. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
^ "Explore Google Chrome Features: Incognito Mode". September 2, 2008. Retrieved September 4, 2008.
^ Falkvinge, Rick (2015-06-18). "Google Chrome Listening In To Your Room Shows The Importance Of Privacy Defense In Depth". Private Internet Access Blog. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
^ Bright, Peter. "Not OK, Google: Chromium voice extension pulled after spying concerns". Ars Technica. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
^ "Diff - 0366a5184a70b3eefb5fcef2c2e13721669f00d8^! - chromium/src - Git at Google". chromium.googlesource.com. Retrieved 26 September 2017.
^ "Chrome Releases: Stable Channel Update". googlechromereleases.blogspot.ca. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
^ ab "Google Chrome, Chromium, and Google". The Chromium Blog. October 1, 2008.
^ "Welcome to the Botnet". 2018-04-07. Archived from the original on 2018-04-07. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
^ "Google Chrome Privacy Notice". Google. December 13, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012
^ abc "Google Reacts to Some Chrome Privacy Concerns". Retrieved September 24, 2008.
^ ab "SRWare Iron webpage". Retrieved October 12, 2008.
^ abc "In The Open, For RLZ". The Chromium Blog. June 2, 2010. Retrieved June 20, 2010.
^ "Google Chrome Unique Identifier Change". March 16, 2010. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
^ Fried, Ina (October 7, 2008). "Google's Omnibox could be Pandora's box". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chrome's privacy settings". Retrieved April 25, 2013.
^ abcdef "Google Chrome Privacy Whitepaper" (PDF). Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "&rlz= in Google referrer: Organic traffic or AdWords?". Retrieved February 27, 2009.
^ Controlled by the setting "Send usage statistics and error reports". Default off.
^ "Turning Off Auto Updates in Google Chrome". Retrieved December 12, 2014.
^ "Tracking DNT". W3C. Retrieved December 17, 2015.
^ "Google and Chrome To Support Do Not Track". Archived from the original on February 26, 2012. Retrieved March 3, 2012.
^ "V8 Benchmark suite". Google Code. Archived from the original on September 4, 2008. Retrieved September 3, 2008.
^ Rupert Goodwins (September 2, 2008). "Google Chrome – first benchmarks. Summary: wow". Archived from the original on September 3, 2008.
^ "Google Chrome Javascript Benchmarks". jrm.cc. September 1, 2008. Archived from the original on January 7, 2012. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Kingsley-Hughes, Adrian (September 2, 2008). "Google Chrome is insanely fast ... faster than Firefox 3.0". ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
^ Alexander Limi (September 2, 2008). "Chrome: Benchmarks and more". Archived from the original on April 24, 2010. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Vygantas Lipskas (March 1, 2009). "Safari 4 vs. Firefox 3 vs. Google Chrome vs. Opera 10, 9.6 vs. Internet Explorer 8, 7". Favbrowser. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Scott M. Fulton, III (October 11, 2010). "Firefox in the dust: Opera poised to reclaim browser performance lead". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved November 6, 2010.
^ Shankland, Stephen (October 7, 2008). "Firefox counters Google's browser speed test". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Eich, Brendan (September 3, 2008). "TraceMonkey Update".
^ Stephen Shankland (November 3, 2008). "Third Chrome beta another notch faster – News". Builder AU. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Resig, John (September 3, 2008). "JavaScript Performance Rundown".
^ Maciej Stachowiak (September 18, 2008). "WebKit blog: Introducing SquirrelFish Extreme". Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Cameron Zwarich (September 18, 2008). "SquirrelFish Extreme has landed!". Archived from the original on April 27, 2009. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Stephen Shankland (September 22, 2008). "Step aside, Chrome, for Squirrelfish Extreme – News". Builder AU. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Charles Ying (September 19, 2008). "SquirrelFish Extreme: Fastest JavaScript Engine Yet". Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ ab Preston Gralla (September 3, 2008). "Three hidden Chrome features you'll love". Archived from the original on September 23, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
^ "DNS prefetching for Firefox". November 8, 2008.
^ Apple Inc. (June 7, 2010). "What's new in Safari 5". Retrieved July 6, 2010.
^ "Internet Explorer 9 Network Performance Improvements". Blogs.msdn.com. March 17, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ João Eiras. "Page prefetcher". userjs.org. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "chrome] Index of /trunk/src/net/spdy – Chromium SPDY client implementation". src.chromium.org. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "SPDY Proxy Examples – The Chromium Projects". www.chromium.org. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Reisn, Charlie (September 11, 2008). "Multi-process Architecture". Retrieved September 12, 2008.
^ "Process Models". The Chromium Projects. Google. September 3, 2008. Retrieved September 12, 2008.
^ Prince, Brian (December 11, 2008). "Google Chrome Puts Security in a Sandbox". eWeek.com. Ziff Davis Enterprise Holdings Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2010.
^ "[webkit-dev] Announcing WebKit2". lists.webkit.org. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Firefox Lorentz beta available for download and testing". Mozilla. April 8, 2010.
^ "Chrome 23 Closes 15 Security Vulnerabilities, Promises Longer Battery Life & Added Do Not Track (DNT)". Retrieved November 9, 2012.
^ Google (2012). "Set your home page". Retrieved May 22, 2012.
^ Fisher, Darin (May 21, 2009). "A Speedier Google Chrome for all users". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ LaForge, Anthony (September 15, 2009). "Google Chrome after a year: Sporting a new stable release". Official Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chromium url_constants.cc". Archived from the original on September 8, 2010. Retrieved September 1, 2010.
^ Pash, Adam (October 2010). "Chrome's About:Labs Renamed to About:Flags, Adds a Warning". LifeHacker. Retrieved October 19, 2010.
^ Rura, Steve (March 2011). "A fresh take on an icon". Retrieved March 22, 2011.
^ Kay, Erik (September 5, 2013). "A new breed of Chrome Apps". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chrome Web Store". Google. May 19, 2010. Retrieved May 24, 2010.
^ Erik Lay (May 19, 2010). "The Chrome Web Store". Google. Retrieved May 24, 2010.
^ Paul, Ryan (December 9, 2010). "Chrome Web Store: a solution in search of a problem?". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Kay, Erik; Boodman, Aaron (February 3, 2011). "A dash of speed, 3D and apps". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ ab "Google Chrome Extensions Blog Announcement". Google. Retrieved February 25, 2010.
^ "Google Chrome Extensions Help Page". Google. Retrieved February 25, 2010.
^ Nield, David. "20 best Chrome extensions". TechRadar. Retrieved May 16, 2012.
^ Developing Chrome Extensions Overview Page
^ "Chrome Web Store Help". Google. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Aaron Boodman (September 9, 2009). "Extensions Status: On the Runway, Getting Ready for Take-Off". Google. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Erik Kay (December 8, 2009). "Extensions beta launched, with over 300 extensions!". Google. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Baum, Nick (January 25, 2010). "Over 1,500 new features for Google Chrome". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Lardinois, Frederic (May 27, 2014). "Chrome For Windows Will Now Only Install Extensions From Google's Web Store". TechCrunch. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
^ "Chrome Web Store - Adblock Plus (Beta)". Chrome.google.com. Retrieved May 16, 2012.
^ "Chrome Web Store - Facebook Messenger". oinkandstuff.com. Retrieved January 1, 2014.
^ Murphy, Glen; Sabec, Mark (October 5, 2009). "A splash of color to your browser: Artist Themes for Google Chrome". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chrome Web Store". Google. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Basic settings: Change browser theme". Google Chrome Help.
^ "Change Chrome languages & translate webpages". support.google.com.
^ Mark Larson (January 8, 2009). "Google Chrome Release Channels". Retrieved January 9, 2009.
^ Mark Larson (January 8, 2009). "Dev update: New WebKit version, new features, and a new Dev channel". Retrieved January 9, 2009.
^ Ian Fette (December 11, 2008). "Thanks For All Your Help". Retrieved May 1, 2015.
^ Anthony Laforge (July 22, 2010). "Release Early, Release Often". Retrieved July 25, 2010.
^ The Chromium Authors. "Chrome Release Channels". Retrieved October 29, 2014.
^ Paul Irish (November 2, 2012). "Chrome Canary for Developers". Retrieved October 29, 2014.
^ Bridge, Henry (August 2, 2010). "Google Chrome in a Coal Mine". Chromium Blog. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
^ Mathews, Lee (July 23, 2010). "Google drops Chrome Canary build down the Chrome mineshaft". Archived from the original on July 25, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2010.
^ "Adding more yellow to the Mac color scheme". blog.chromium.org. May 2, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012 .
^ ab Protalinski, Emil (January 10, 2013). "Google launches Chrome Beta channel for Android 4.0+ phones and tablets, releases version 25". The Next Web. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chrome beta for Android on Google Play". Play.google.com. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
^ "Google Launches Dev Channel for Chrome on Android". Chrome Story. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
^ David Dorwin (May 14, 2009). "Google Update Releases Update Controls". Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ "Alternate (offline) Google Chrome installers for Windows - Chrome Help".
^ "Get a fast, free web browser". Google.com. Google. Retrieved February 17, 2017.
^ "Google Help page "Managing updates in Google Software Update"".
^ "Tour of the Chromium Buildbot Waterfall - The Chromium Projects". Retrieved December 2, 2014.
^ ab "Version 42 Stable Release". Chrome Releases. Google. April 14, 2015. Retrieved December 28, 2015.
^ abc "Chromium Development Calendar and Release Info". The Chromium Projects. Retrieved May 1, 2015.
^ Mike Frysinger (March 14, 2014). "Version Numbers". The Chromium Projects. Retrieved May 1, 2015.
^ Anthony LaForge (December 16, 2010). "Chrome Release Cycle -12/16/2010". Google Slides. Retrieved May 1, 2015.
^ "Version 42 Developer Update". Chrome Releases. Google. February 26, 2015. Retrieved December 28, 2015.
^ "Issue 143: Handle color profiles in tagged images". Code.google.com. September 2, 2008. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
^ "Google Chrome Easter Egg T-Rex Mini Game". Business Insider.
^ "Play Google Chrome's Secret Offline Game".
^ "How do I find the secret dinosaur game on Google Chrome when my internet connection is down?". RadioTimes.
^ "Google Chrome's 'Unable to connect to the Internet' page has a hidden endless runner game". The Independent.
^ "Issue 462221 - chromium - Disable offline game (T-Rex) if device is enrolled - Monorail". Chromium.org. Google. February 26, 2015. Retrieved July 27, 2016.
^ abc "Download and install Google Chrome". Google Help. See system requirements. Retrieved April 20, 2016.
^ abc Google (November 18, 2014). "Stable Channel Update". Retrieved November 18, 2014.
^ Google. "64-bit Support – The Chromium Projects". Retrieved March 5, 2012.
^ "Download Chrome for Linux". Google.
^ Google. "Try out the new 64-bit Windows Canary and Dev channels". Retrieved July 1, 2014.
^ Google. "Announcing the Chrome 64-bit Beta Channel for Windows!". Retrieved August 11, 2014.
^ "64 bits of awesome: 64-bit Windows Support, now in Stable!". August 26, 2014. Retrieved August 27, 2014.
^ Google. "[chromium-dev] Yesterday's Mac canary was 64-bit". Retrieved July 1, 2014.
^ Google. "Re: [chromium-dev] Re: Chromium 64-bit on Mac OS". Retrieved July 1, 2014.
^ Google (October 9, 2014). "Beta Channel Update". Retrieved October 10, 2014.
^ "Install Chrome for Android Beta – Google Chrome Help". Google. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
^ abc "Beta version of Chrome for Android 4.0 released". www.neowin.net. Retrieved February 9, 2012 .
^ abcde "Google Operating System: Chrome for Android". googlesystem.blogspot.com. February 27, 2004. Retrieved February 9, 2012 .
^ abcd "Google Chrome for Android – 23 Questions and Answers". Chrome Story. Retrieved February 9, 2012
^ abcde Peter Beverloo (January 30, 2012). "Bringing Google Chrome to Android". Retrieved February 9, 2012 .
^ "Security overview". Google. Retrieved February 9, 2012 .
^ "Google Chrome for Android: Remote Debugging". Google. Retrieved February 9, 2012 .
^ Lardinois, Frederic (April 17, 2012). "Chrome For Android Gets Desktop View, Home Screen Bookmarks, File Downloads".
^ "Google Chrome for Android comes out of beta, Hits Play today". Engadget. AOL. June 27, 2012. Retrieved June 27, 2012 .
^ "Chrome for Android Update". Googlechromereleases.blogspot.hu. September 26, 2012. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
^ "Chrome Beta for Android". play.google.com. May 26, 2013. Retrieved July 4, 2013.
^ Dylan F. Tweney (November 19, 2009). "Gadget Lab Hardware News and Reviews Google Chrome OS: Ditch Your Hard Drives, the Future Is the Web". Wired. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 9, 2014. Retrieved November 22, 2009.
^ Sengupta, Caesar; Papakipos, Matt (November 19, 2009). "Releasing the Chromium OS open source project". Official Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Stokes, Jon (January 20, 2010). "Google talks Chrome OS, HTML5, and the future of software". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Womack, Brian (July 8, 2009). "Google to Challenge Microsoft With Operating System". Bloomberg. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
^ Hansell, Saul (July 8, 2009). "Would you miss Windows with a Google operating system?". New York Times. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
^ Pichai, Sundar; Upson, Linus (July 7, 2009). "Introducing the Google Chrome OS". Official Google Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Mediati, Nick (July 7, 2009). "Google Announces Chrome OS". PC World. IDG. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
^ "Chrome entry - Apple's App Store".
^ "Google Chrome on iOS Hits #1 Free App". Forbes.
^ "iOS 8 WebKit changes finally allow all apps to have the same performance as Safari".
^ Steve Kovach (May 8, 2013). "Here's Even More Evidence That Google Is Trying To Take Over The iPhone". Business Insider. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
^ Reisinger, Don (July 18, 2012). "Chrome already nabs 1.5 percent of iOS browser market". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Chrome's Share of iOS Usage Doubles Year-Over-Year to 3%". Mac Rumors. October 11, 2013. Retrieved April 21, 2014.
^ "Google ends 32-bit Linux support for Chrome". OSNews.
^ "Chrome stops declaring Linux systems obsolete - The H Open: News and Features". H-online.com. February 14, 2013. Retrieved March 30, 2013.
^ Pawliger, Marc (November 10, 2015). "Updates to Chrome platform support". Chrome Blog. Google. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ Cunningham, Andrew (April 14, 2016). "Chrome 50 ends support for Windows XP, OS X 10.6, other old versions". ArsTechnia. Archived from the original on May 5, 2016. Retrieved October 9, 2016.
^ "Stable Channel Update". googlechromereleases.blogspot.com. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
^ "Google Chrome 49.0.2623.112". filehippo.com. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
^ Newman, Jared. "Google Chrome Gets Early Metro-Style App for Windows 8". PCWorld. IDG. Retrieved June 13, 2012.
^ "Google is building Chrome OS straight into Windows 8". The Verge. Retrieved October 5, 2013.
^ "Unable to open Google Chrome in windows 8 mode - Google Product Forums". Retrieved September 29, 2016.
^ "Chrome no longer supports Mac OS X 10.5". Google. Archived from the original on March 29, 2015.
^ "Chrome updates on Mac 32-bit". Chrome help. Google.
^ "Google to Discontinue 32-bit Chrome for Mac Next Month". OMG! Chrome!.
^ Moore, Matthew (September 2, 2008). "Google Chrome browser: Review of reviews". Daily Telegraph. Retrieved September 24, 2011.
^ Liedtke, Michael (September 3, 2008). "Google polishes product line with Chrome browser". Associated Press. Archived from the original on June 23, 2012.
^ Jaroslovsky, Rich (February 25, 2010). "Browser Wars: The Sequel". BusinessWeek.
^ "Thoughts on Chrome & More". John's Blog. September 1, 2008. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ Collins, Barry (September 2, 2008). "Mozilla: Google's not trying to kill us". PC Pro. Dennis Publishing. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ Mediati, Nick (September 3, 2008). "Google Chrome Web Browser". PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 7, 2008.
^ "Top 5 Browsers from December 2010 to December 2011". StatCounter. Retrieved January 8, 2012.
^ "Top Browsers Per Country, July 2017". Statcounter. 2017. Retrieved 2017-08-02.
^ "Top 9 Desktop Browsers from W01 2015 to W27 2016". StatCounter.
^ For additional sources see Usage share of web browsers#Summary table
^ "Global Web Browser Marketshares". Clicky Analytics. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Chrome is world's number one browser for a day". StatCounter. March 21, 2012.
^ "Chrome overtakes Internet Explorer as No. 1 browser -- maybe". CNN. May 21, 2012. Retrieved May 21, 2012.
^ Pachal, Peter (May 21, 2012). "Google Chrome Now the No. 1 Browser in the World". mashable.com.
^ "Chrome tops 310 million users, almost 100% growth over last year". June 28, 2012.
^ "Stats Counter US Monthly bar graph". June 2013. Retrieved July 25, 2013.
^ Fox, Zoe (August 14, 2013). "43% of Global Web Surfers Choose Google Chrome".
^ "Top 5 Desktop browser in June 2018". StatCounter. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
^ "Change MSI from a wrapper to "full" MSI". Google. January 4, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ Paul, Ryan (December 16, 2010). "Google offering MSI to simplify Chrome enterprise deployment". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
^ "Google Update for Enterprise – Google Help". Google. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
^ "Issue 2423 – chromium – Windows Roaming Profile support – An open-source browser project to help move the web forward. – Google Project Hosting". Google. September 17, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2012.
^ "Home (Chromium Developer Documentation)". Chromium Developer Documentation. 2009. Retrieved May 5, 2009.
^ "Chromium Terms and Conditions". Google Code. September 2, 2008. Archived from the original on September 4, 2008. Retrieved September 3, 2008.
^ Chromium Project (March 2011). "ChromiumBrowserVsGoogleChrome". Retrieved July 10, 2011.
^ McAllister, Neil (September 11, 2008). "Building Google Chrome: A first look". InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 13, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.As the name suggests, Chromium is a rawer, less polished version of Chrome. The UI is mostly identical, with only a few very minor visual differences. [...] The most readily evident difference is the logo, which sheds the Google colors in favor of a subdued blue design.
^ "Differences between Google Chrome and Linux distro Chromium". Google. 2010. Retrieved September 1, 2010.
^ "Chromium revision log: Changes in revision 271531". May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 24, 2014.
^ "Change log for Chromium wiki showing removal of a part that said PDF support were different between Chromium and Google Chrome". May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 24, 2014.
^ Garthwaite, Emily. "Google throws PDFium into the open source community". IT Pro Portal. Retrieved September 11, 2016.
^ "Developer's Guide - Google Chrome". Developer.chrome.com. Retrieved February 17, 2014.
^ "Chrome Web Store". chrome.google.com.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Google Chrome. |
Official website
Google Chrome release channels (choice of stable / beta / dev / canary builds)- History of Google Chrome on "Chrome Time Machine"
- Google Chrome Releases blog
 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP